Google’s AI Advancements: Leading the Future of Search
Smart World News |
At Google I/O 2025, Google presented a grand spectacle of its search empire's self-revolution and AI's comeback. In this era of information overload, "search" has long been a core method for people to obtain information. As one of the world's leading search engines, Google has consistently explored the boundaries of the search experience. Recently, Google officially launched "Real-Time AI Search," simultaneously unlocking two new input functions: video and voice. This completely breaks the limitations of traditional "keyword typing" searches, allowing information acquisition to move from "active description" to "instant interaction," bringing users a more efficient and context-appropriate search experience.
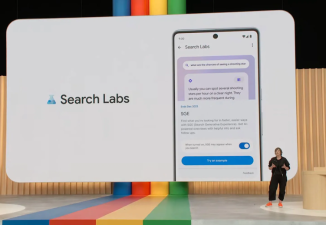
Real-Time AI Search
More Than Just "Searching," It's About "Understanding" Unlike traditional searches that require users to accurately input keywords and then sift through massive amounts of results, Google's "Real-Time AI Search" focuses on "real-time AI understanding and integration." It relies on Google's upgraded large language model and multimodal recognition technology, enabling it to analyze user intent in real-time after a search request and directly integrate information from authoritative websites, databases, and professional platforms, presenting it as a "structured answer" rather than simply listing links.
For example, when a user searches for "best wireless headphones of 2024," a traditional search would display dozens of review articles. However, in real-time AI mode, the system first identifies three core needs: "2024," "best," and "wireless headphones." Then, it retrieves data in real-time from recent professional review organizations (such as CNET and Wirecutter) and user review platforms (such as Amazon and Reddit), automatically filtering out the top 5 products with the highest overall ratings. It clearly lists the core parameters (battery life, noise cancellation, sound quality), price range, and purchase channels for each product—essentially letting AI directly handle the "information filtering + integration and summarization" steps, eliminating the need for users to click through links one by one to find key information.
Furthermore, real-time AI mode supports "multi-round follow-up questions." If a user asks, "Which one is suitable for sports?" after seeing the headphone recommendations, the AI will supplement the analysis with further information on each headphone's waterproof rating, wearing stability, and other sports-related characteristics, achieving a "continuous search," much like conversing with a professional "information consultant."
Key New Features: Natural Voice Interaction, Video "What You See Is What You Search"
The two major input features upgraded in this update—optimized voice input and video input—make search scenarios truly seamless, completely eliminating reliance on the keyboard.
- Voice Input: From "Command-Based" to "Conversational"
Past voice searches were mostly limited to short commands (such as "nearby cafes" or "today's weather"), but Google's upgraded voice input supports "long conversations in natural language." Users don't need to deliberately simplify their expressions; they can describe their needs as if in everyday conversation, for example, "I'm taking my family to Beijing for 3 days this weekend and I'd like to find suitable attractions for a 5-year-old, as well as recommendations for cost-effective family hotels, preferably close to the attractions."
AI will break down the key information in the sentence in real time: destination (Beijing), duration (3 days), target audience (with a 5-year-old child), need 1 (family-friendly attractions), need 2 (high-value family-friendly hotels near attractions), and output targeted integrated results—for example, first listing family-friendly attractions such as the Forbidden City, Beijing Zoo, and China Science and Technology Museum, noting opening hours and suitable activities for children, then recommending hotels within 3 kilometers of the attractions with a rating of 4.5 or higher and including children's facilities, and even adding suggestions on "transportation routes between attractions."
Meanwhile, voice input also supports "environmental adaptation." In noisy scenarios such as shopping malls and streets, AI can filter background noise through noise reduction algorithms to accurately recognize the user's voice, avoiding search bias caused by environmental interference.
- Video Input: "What You See Is What You Search," Solving the Pain Point of "Unable to Describe"
"I want to search for something, but I don't know its name, and I can't describe it clearly in words"—this is a search problem many people encounter. Google's newly launched "video input" function precisely solves this pain point, achieving "what you see is what you search."
Users simply need to open the Google Search app, click the "Video Input" button in Real-Time AI mode, and record a 10-15 second video (no need to record the entire video, just a clip) of the object or scene they want to search for. AI will analyze the video content using image recognition and object detection technology, identifying the core object and matching relevant information.
For example:
Seeing a uniquely packaged imported snack in a supermarket, but unsure of its flavor or ingredients, record a video. AI will identify the snack's brand, flavor, and even provide the ingredient list, calorie information, and user reviews.
Seeing a uniquely designed car on the street, recording a video will quickly provide information such as the car model, manufacturer, price, and performance specifications.
Encountering an unfamiliar plant or insect, recording a video will identify the species name, growth habits (or whether it is poisonous), overcoming outdoor "cognitive blind spots."
Currently, video input supports the recognition of common objects, products, plants and animals, landmarks, and other scenes. It will be gradually expanded to "scene analysis" (such as recording a restaurant environment to recommend dishes).
Getting Started: Real-Time AI Mode User Guide
Google Search's Real-Time AI mode is currently being rolled out to Android and iOS users in select regions globally (initially including the US, UK, and Canada). Users need to update their Google Search app to the latest version (Android V14.5+, iOS V14.3+). The specific steps are as follows:
Enable Real-Time AI Mode: Open the Google Search app. The "Real-Time AI" entry will appear at the top of the homepage (if not, enable the "AI Enhanced Search" function in settings). Tap it to enter the mode.
Choose an Input Method:
- Voice Input: Tap the "Microphone" icon within the mode and describe your needs directly in natural language. The AI will automatically begin analysis after you finish speaking.
- Video Input: Tap the "Camera" icon to switch to "Video" mode. Record a video of your target for 10-15 seconds (keep the image clear and avoid shaking). After recording, tap "Confirm." The AI will recognize the video content.
- Text Input: If you prefer text, you can type directly in the input box. The AI will provide a "structured answer." Output Results in Format;
- Getting and Interacting with Results: After the AI generates the results, you can swipe to view detailed information. If you have further needs, you can click the "Ask a Follow-up Question" button to ask questions (such as "Recommend another pair of headphones in the same price range"), enabling multi-round interaction;
- Close Mode: Click the "Close" button in the upper right corner of the page to return to the traditional search interface.
Note that because the real-time AI mode requires multimodal recognition and cloud computing resources, you need to ensure your device is connected to the internet (Wi-Fi or 5G network is recommended to avoid excessive data consumption). Some regions may not be supported due to network conditions or policies.
Reconstructing Search Logic: A Leap from "Keywords" to "Contextualization"
Google's launch of the real-time AI mode is essentially a revolution in "search logic"—in the past, the core of search was "users adapting to the system" (users needed to learn how to "please" the search engine with precise keywords); now, the system begins to "adapt to users," using AI to understand scenarios and identify needs, transforming search from a "tool" into a "proactive service."
For users, this means a significant improvement in "information retrieval efficiency": no more time spent organizing keywords and filtering links; whether through voice descriptions, video recordings, or casual conversational follow-up questions, accurate results can be obtained quickly, especially suitable for fragmented scenarios (such as using voice to search for information during commutes or using video to search for products while shopping).
From an industry perspective, this upgrade by Google also provides direction for the future development of search engines: multimodal input (voice, video, image) + real-time AI integration may become the mainstream trend. In the future, search may no longer be limited to "in-app operations" and may even be integrated into wearable devices such as smartwatches and smart glasses, achieving a seamless experience of "searching anytime, anywhere, and whatever you see."
However, the new feature also faces some challenges, such as the "accuracy and authority" of AI information (how to avoid the integration of erroneous information) and user privacy protection (storage and use of voice and video data). Google stated that it currently ensures the accuracy of information through a "prioritizing authoritative sources" mechanism and uses end-to-end encryption technology to protect user input data, and will continue to optimize algorithms and privacy policies.
For ordinary users, the launch of real-time AI mode undoubtedly makes "obtaining information" simpler and more efficient. As the function is gradually improved and the regional coverage expands, perhaps soon, "open Google, tap and talk" will become a new search habit, allowing information to truly serve the "scenario" rather than being limited to the "keyboard".





